EV Charging
Technology segments shaping the future
To meet the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and to achieve decarbonization targets, it is essential to establish better charging infrastructure through the design and installation of efficient EV charging systems.
Conversion from AC to DC in the charging station rather than in the car’s on-board charger enables substantially faster charging speeds. This is why DC EV chargers have become mainstream products: today’s chargers are compatible with 400V or 800V EV batteries, and the latest ultra-fast charging stations provide a power output of over 350kW.
Silicon carbide (SiC) technology is the ideal choice for this application because of its high efficiency and ability to handle higher voltage and temperature than silicon MOSFETs or IGBTs can.
A system solution from onsemi
The block diagram shows a DC EV charger solution created by onsemi: the functional blocks shown in orange are performed by onsemi products, including SiC discrete MOSFETs, IGBTs, power modules and isolated gate drivers.
Use the menu below to see the parts related to each section on the diagram.
Products from onsemi support the most popular topologies for each power stage:
- PFC topologies - T-type neutral point clamped, active neutral point clamped, or Vienna rectifier
- Isolated DC-DC converter topologies – full-bridge LLC, phase-shifted LLC, dual active bridge, or dual active bridge CLLC
onsemi System Solution Guide for DC EV Chargers A detailed design guide to ultra-fast DC EV chargers and a comprehensive list of recommended products can be found in the onsemi System Solution Guide. |
SiC for EV chargers: higher efficiency and thermal performance
EV charger manufacturers were among the first companies to adopt SiC semiconductor technology: they valued its higher efficiency, faster switching, and ability to withstand higher operating temperature than silicon power devices.
onsemi offers unique value in SiC technology with its breadth and depth of high-efficiency intelligent power solutions. Backed by years of manufacturing expertise, a vertical supply chain benefiting from substantial capital investment, and expanded R&D efforts, onsemi is a market leader in SiC.
SiC solutions from onsemi for EV charging give customers the flexibility to choose discrete or module solutions based on their system requirements. Product offerings include SiC diodes, SiC MOSFETs, SiC modules, and hybrid silicon/SiC modules, supported by a complete ecosystem of design tools. These include SiC MOSFET SPICE Models and SiC Diode SPICE Models.
Unique information resources to support your EV charger design
Are you starting your first design based on SiC components? onsemi experts have described when, where and how to use SiC MOSFETs in place of the silicon alternative.
And Future Electronics’ Riccardo Collura has explained the topologies available for bidirectional EV chargers. EV charging stations can benefit from the increased voltage headroom provided by the latest EliteSiC MOSFETs from onsemi, which feature a 1700V breakdown voltage rating.
Design Blueprint: SiC-Based 25kW DC Charger Board for EV Charging Stations » See design guide: Developing a 25-kW SiC-based fast DC charger |
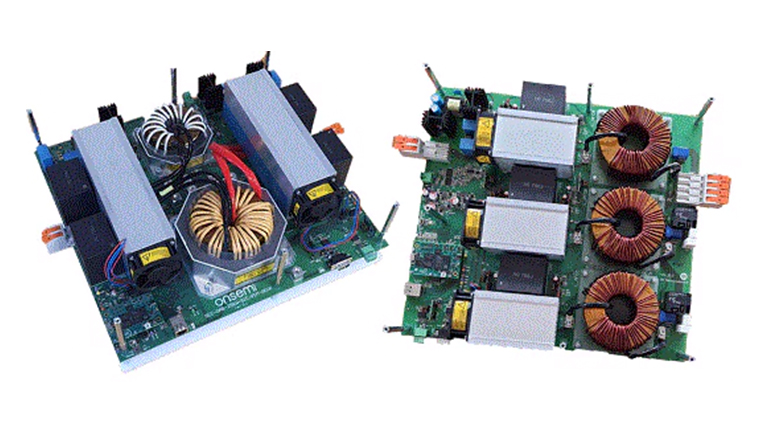
This reference design kit implements a design for a 25kW fast DC electric vehicle (EV) charger based on an integrated silicon carbide (SiC) power module. It takes full advantage of the advanced SiC material to reduce power losses and perform fast switching, resulting in very high efficiency and power density.
This full SiC solution consists of PFC and DC-DC converter stages based on multiple 1200V NXH010P120MNF1 half-bridge SiC modules. Featuring ultra-low on-resistance and minimal parasitic inductance, these modules significantly reduce conduction loss and switching loss. Controlled by a powerful Universal Controller Board (UCB), the system can supply a maximum 25kW over an output-voltage range of 200V to 1000V (for 400V or 800V EV batteries), operating at 96% efficiency.
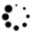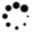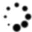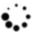
Design Blueprint: CLLC Stage of 6.6kW On-Board Charger Kit part number: SEC-6K6W-CLLC-GEVK |
This evaluation kit is a reference design for the CLLC bidirectional DC-DC converter stage of an EV’s onboard charger (OBC). The reference design consists of multiple boards which provide for separation between the control and power conversion functions.
The system uses the automotive-grade NVHL040N120SC1 and NVHL020N090SC1 silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFETs. Thanks to the advanced SiC material, these MOSFETs offer higher power density, higher switching frequency, and more efficient operation than silicon-based solutions.
NCV57000 galvanically isolated gate drivers drive the MOSFETs. They feature separate drive outputs and fault detection with reinforced safety insulation.
An NCV4390 power controller implements the CLLC topology, allowing bidirectional power transfer switched by a microcontroller’s control pin: this means that the system can swap between grid-to-battery or battery-to-grid modes while maintaining the correct output voltage and current.
The system also uses onsemi products for the power rails (NCV890100, NCV4274, NCV8715) and the analog signal chain (NCV210, NCV2901, NCV2003, NCV33204), as well as bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), diodes and ESD protection devices.
Related Products